Example
For programmers coming from GCC or Clang to Visual Studio, or programmers more comfortable with the command line in general, you can use the Visual C++ compiler from the command line as well as the IDE.
But I'm not able to uninstall Unity, IIS, SQL with this command line: 'C: Program Files (x86) Microsoft Visual Studio Installer vsinstaller.exe' /uninstall -quiet -norestart. I think it's because all these components are installed independently from VS Studio and are in different install folders. Devenv allows you to build your solution or project using command line. It also allows related multiple operations such as clean solution, rebuild solution or deploy solution etc. To execute commands, you need to open Visual Studio command prompt available inside visual studio tools under all programs of start menu. Add Visual Studio Command Prompt To Visual Studio 2015. If you need to add Visual Studio Command Prompt (essentially just a command window, but pre-prepared with all your Visual Studio paths), this is how you add it to Visual Studio 2015. Open Tools - “External Tools”. Enter the following information into the new tool.
If you desire to compile your code from the command line in Visual Studio, you first need to set up the command line environment. This can be done either by opening the Visual Studio Command Prompt/Developer Command Prompt/x86 Native Tools Command Prompt/x64 Native Tools Command Prompt or similar (as provided by your version of Visual Studio), or at the command prompt, by navigating to the VC subdirectory of the compiler's install directory (typically Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual Studio xVC, where x is the version number (such as 10.0 for 2010, or 14.0 for 2015) and running the VCVARSALL batch file with a command-line parameter specified here.
Note that unlike GCC, Visual Studio doesn't provide a front-end for the linker (link.exe) via the compiler (cl.exe), but instead provides the linker as a separate program, which the compiler calls as it exits. cl.exe and link.exe can be used separately with different files and options, or cl can be told to pass files and options to link if both tasks are done together. Any linking options specified to cl will be translated into options for link, and any files not processed by cl will be passed directly to link. As this is mainly a simple guide to compiling with the Visual Studio command line, arguments for link will not be described at this time; if you need a list, see here.
Note that arguments to cl are case-sensitive, while arguments to link are not.
[Be advised that some of the following examples use the Windows shell 'current directory' variable, %cd%, when specifying absolute path names. For anyone unfamiliar with this variable, it expands to the current working directory. From the command line, it will be the directory you were in when you ran cl, and is specified in the command prompt by default (if your command prompt is C:src>, for example, then %cd% is C:src).]
Assuming a single source file named main.cpp in the current folder, the command to compile and link an unoptimised executable (useful for initial development and debugging) is (use either of the following):
Assuming an additional source file 'niam.cpp' in the same directory, use the following:
You can also use wildcards, as one would expect:
To rename or relocate the executable, use one of the following:
Both /o and /Fe pass their parameter (let's call it o-param) to link as /OUT:o-param, appending the appropriate extension (generally .exe or .dll) to 'name' o-params as necessary. While both /o and /Fe are to my knowledge identical in functionality, the latter is preferred for Visual Studio. /o is marked as deprecated, and appears to mainly be provided for programmers more familiar with GCC or Clang.
Note that while the space between /o and the specified folder and/or name is optional, there cannot be a space between /Fe and the specified folder and/or name.

Similarly, to produce an optimised executable (for use in production), use:
Finally, to produce a platform-specific optimized executable (for use in production on the machine with the specified architecture), choose the appropriate command prompt or VCVARSALL parameter for the target platform. link should detect the desired platform from the object files; if not, use the /MACHINE option to explicitly specify the target platform.
Any of the above will produce an executable with the name specified by /o or /Fe, or if neither is provided, with a name identical to the first source or object file specified to the compiler.
Automate Visual Studio Installation With A Response File
To compile a file(s) without linking, use:
This tells cl to exit without calling link, and produces an object file, which can later be linked with other files to produce a binary.
There are other valuable command line parameters as well, which it would be very useful for users to know:
For anyone more familiar with *nix systems and/or GCC/Clang, cl, link, and other Visual Studio command line tools can accept parameters specified with a hyphen (such as -c) instead of a slash (such as /c). Additionally, Windows recognises either a slash or a backslash as a valid path separator, so *nix-style paths can be used as well. This makes it easy to convert simple compiler command lines from g++ or clang++ to cl, or vice versa, with minimal changes.
Of course, when porting command lines that use more complex g++ or clang++ options, you need to look up equivalent commands in the applicable compiler documentations and/or on resource sites, but this makes it easier to get things started with minimal time spent learning about new compilers.
In case you need specific language features for your code, a specific release of MSVC was required. From Visual C++ 2015 Update 3 on it is possible to choose the version of the standard to compile with via the /std flag. Possible values are /std:c++14 and /std:c++latest (/std:c++17 will follow soon).
Note: In older versions of this compiler, specific feature flags were available however this was mostly used for previews of new features.
-->
If you experience a catastrophic error and can't repair or uninstall Visual Studio, you can run the InstallCleanup.exe tool to remove installation files and product information for all installed instances of Visual Studio 2017, Visual Studio 2019, or Visual Studio 2022.
Warning
Use the InstallCleanup tool only as a last resort if repair or uninstall fail. This tool might uninstall features from other Visual Studio installations or other products, which then might also need to be repaired or reinstalled.

Run InstallCleanup.exe
You can use either of the following command-line switches with the InstallCleanup.exe tool:
| Switch | Behavior |
|---|---|
-i | This switch is the default if no other switch is passed. It removes only the main installation directory and product information. Use this switch if you intend to reinstall the same version of Visual Studio after you run the InstallCleanup.exe tool. |
-f | This switch removes the main installation directory, product information, and most other features installed outside the installation directory, that might also be shared with other Visual Studio installations or other products. Use this switch if you intend to remove Visual Studio without reinstalling it later. |
Here's how to run the InstallCleanup.exe tool:
Close the Visual Studio Installer.
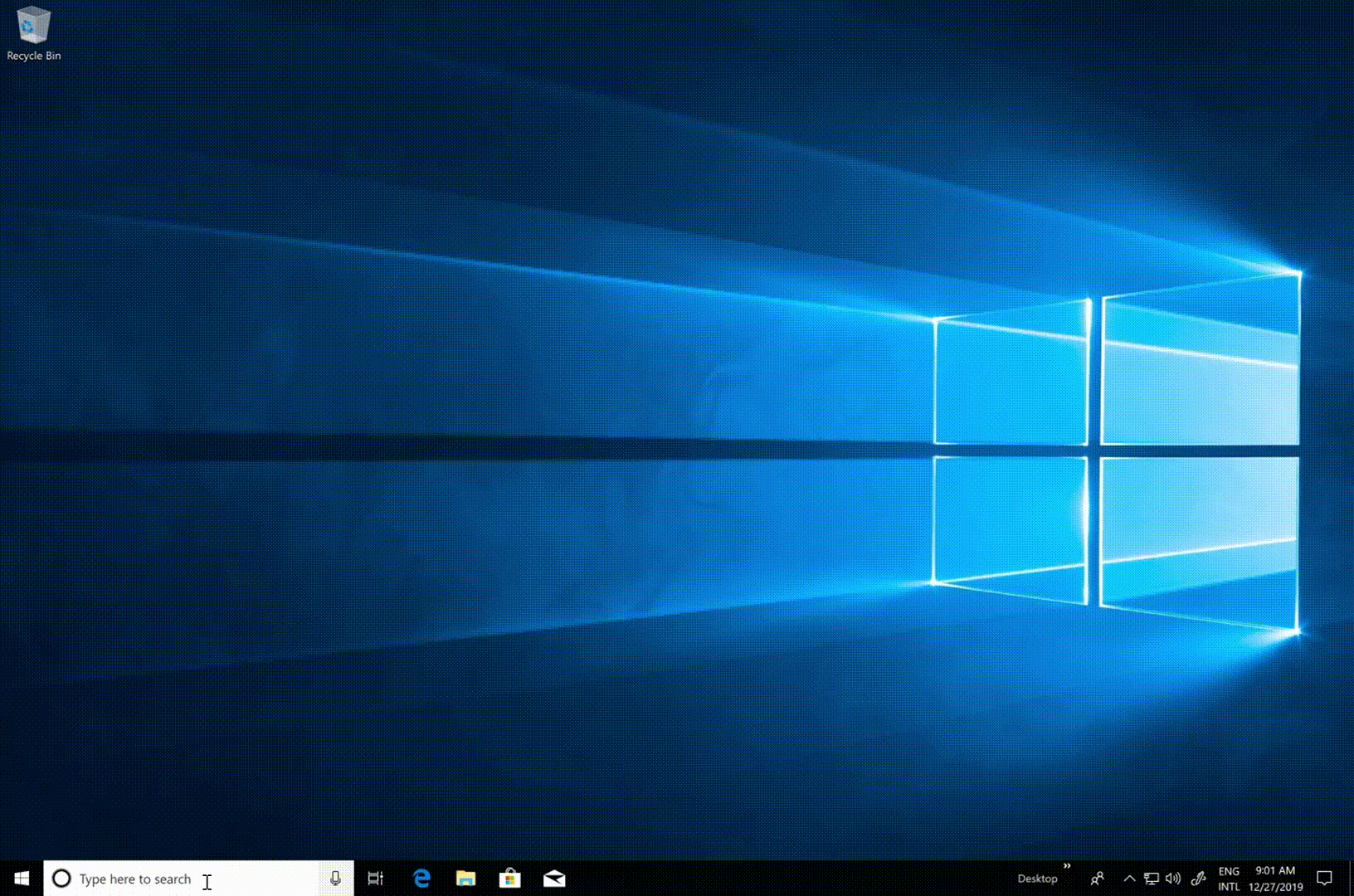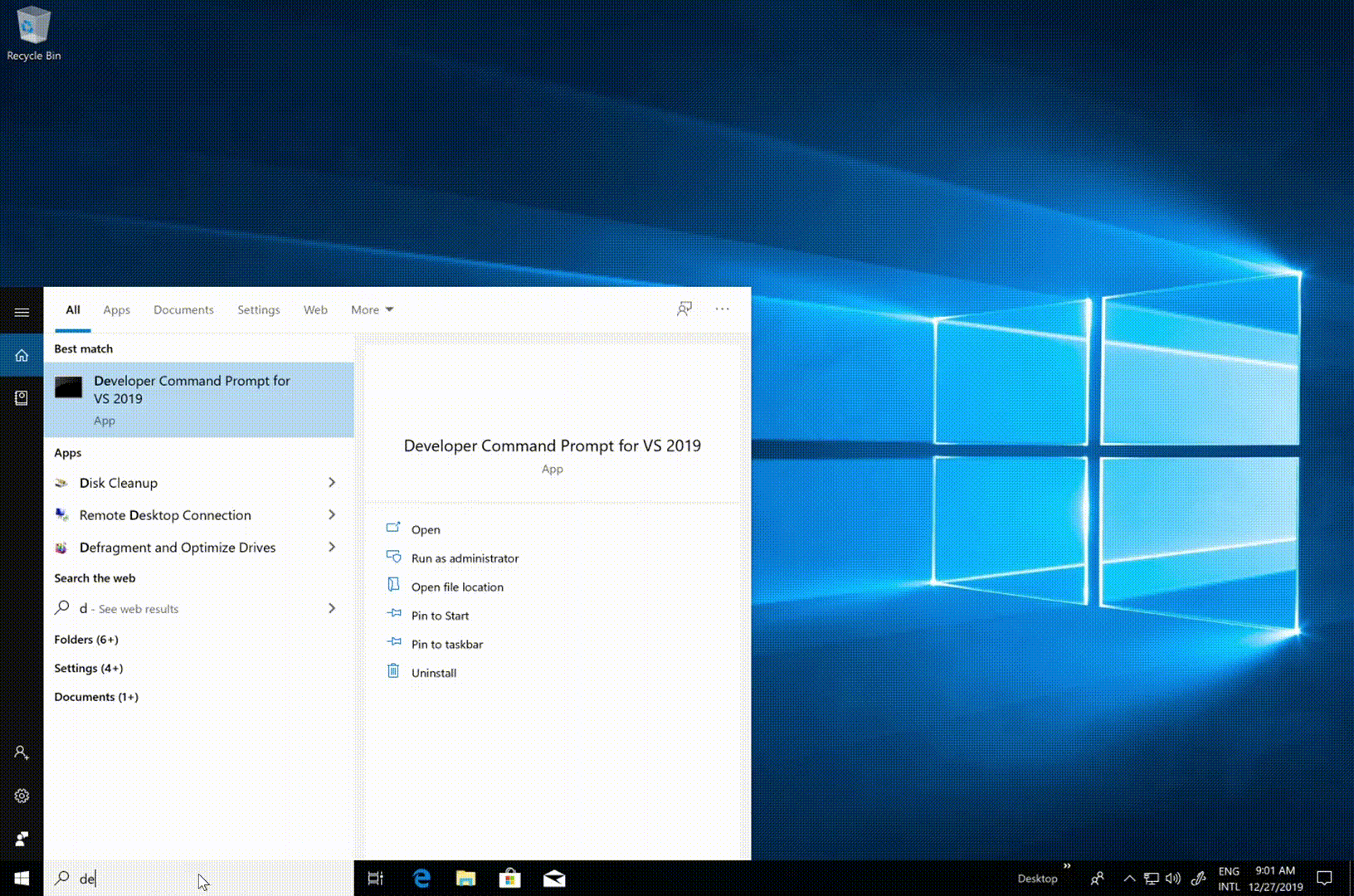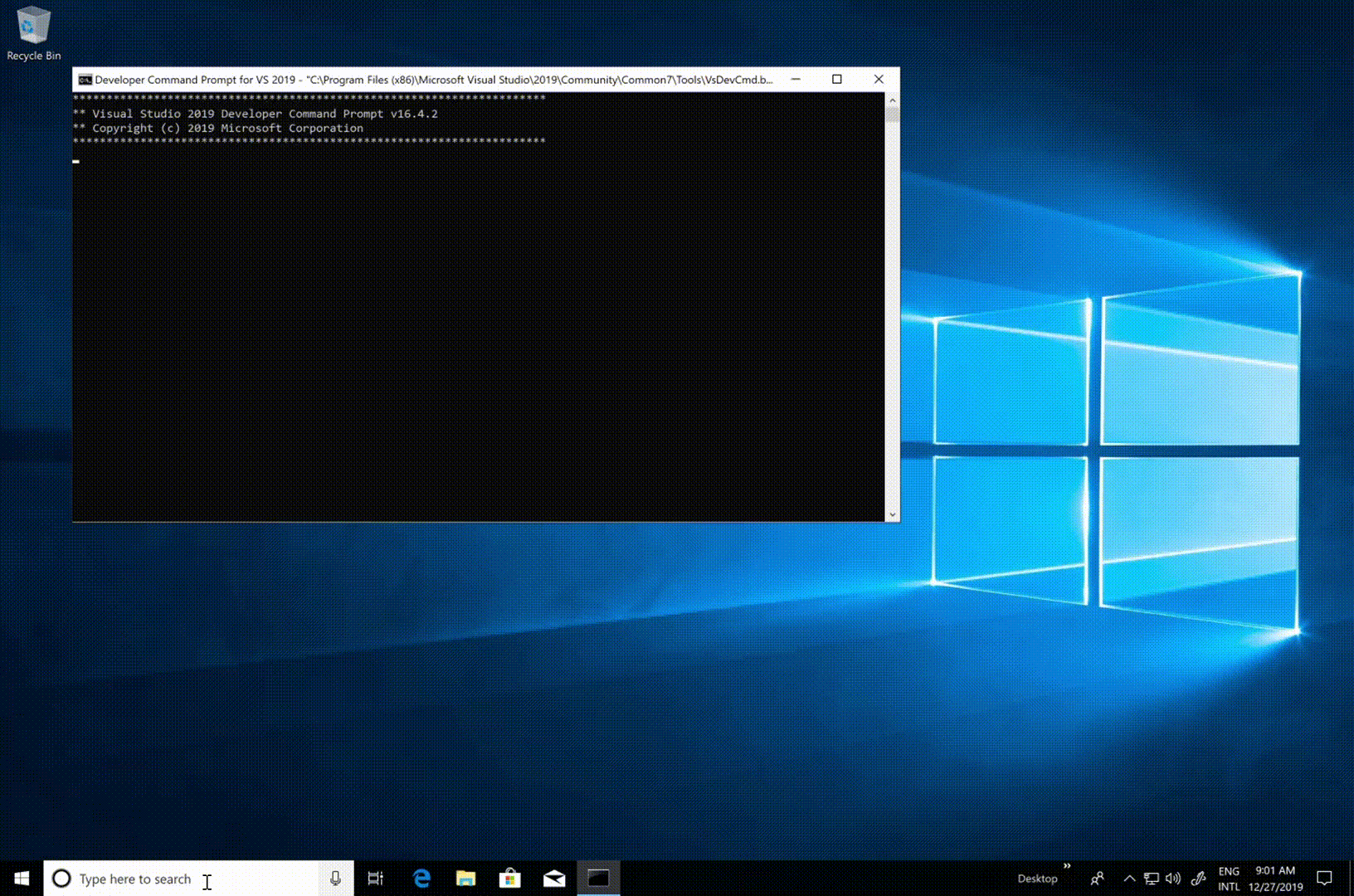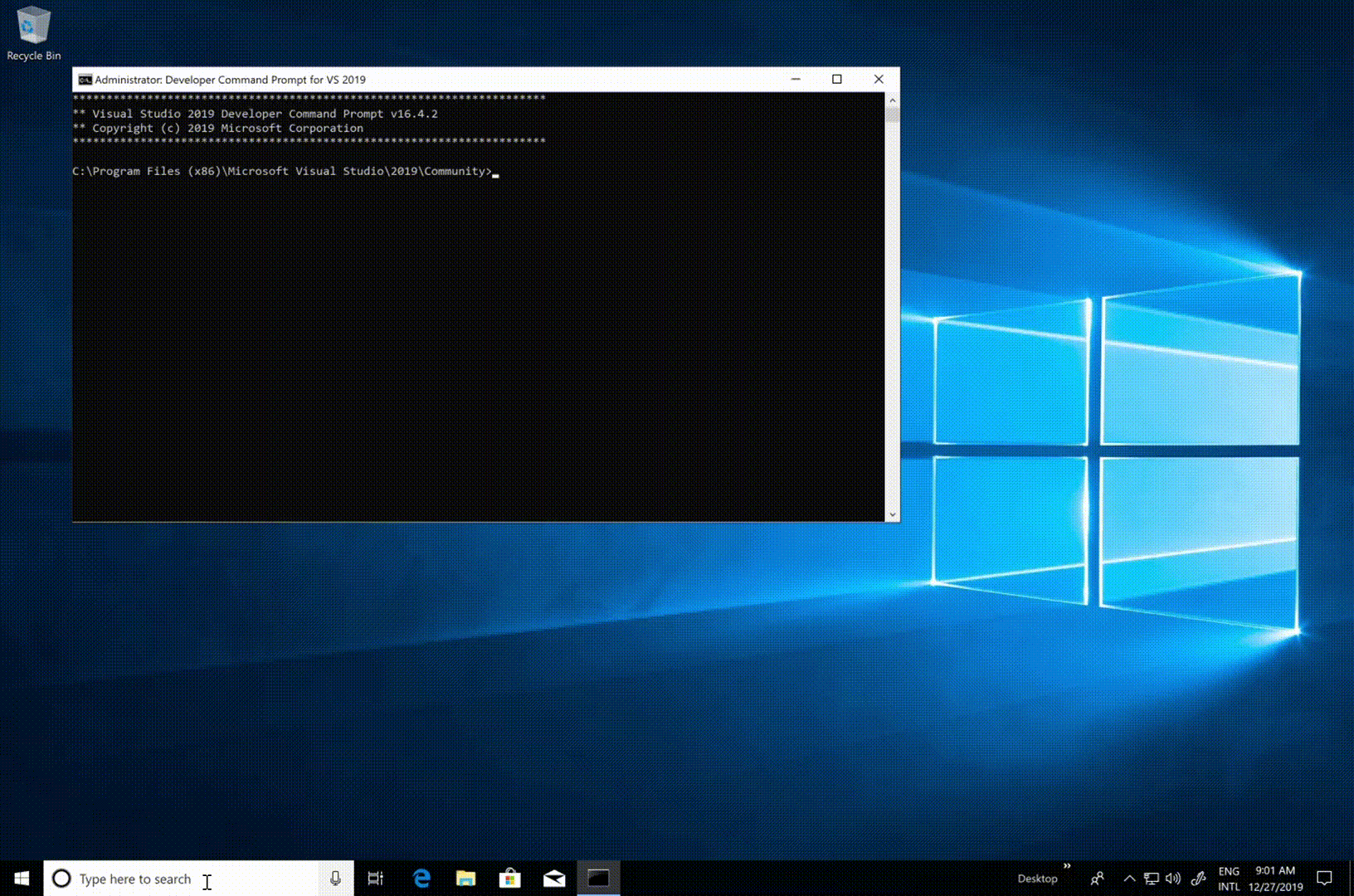
Open an administrator command prompt. To open an administrator command prompt, follow these steps:
- Type cmd in the 'Type here to search' box.
- Right-click Command Prompt, and then choose Run as administrator.
Enter the full path of the
InstallCleanup.exetool and add the command-line switch you prefer. By default, the path of the tool is as follows. The double quotes enclose a command containing spaces:Note
If you can't find
InstallCleanup.exeunder the Visual Studio Installer directory, which is always located at%ProgramFiles(x86)%Microsoft Visual Studio, here's what to do next. Follow the instructions to install Visual Studio. Then, when the workload selection screen is displayed, close the window and follow the steps on this page again.
Get support
Sometimes, things can go wrong. If your Visual Studio installation fails, see Troubleshoot Visual Studio installation and upgrade issues for step-by-step guidance.
How To Pass Command Line Argument In Visual Studio ( C Program )
We also offer an installation chat (English only) support option for installation-related issues.
Here are a few more support options:
Starting Visual Studio From A Command Prompt - Stack Overflow
- Report product issues to us via the Report a Problem tool that appears both in the Visual Studio Installer and in the Visual Studio IDE.
- Suggest a feature, track product issues, and find answers in the Visual Studio Developer Community.
- Use your GitHub account to talk to us and other Visual Studio developers in the Visual Studio conversation in the Gitter community.
Comments are closed.